How to Improve Reimbursement Rates Without Extra Work
65oui8jazfl8fvhx • February 6, 2025
The body content of your post goes here. To edit this text, click on it and delete this default text and start typing your own or paste your own from a different source.

In the world of medical billing, accuracy is everything. One of the most serious issues practices face is upcoding—the act of billing for a higher-level service than what was actually provided. While sometimes intentional, upcoding often happens by mistake, leaving providers exposed to audits, penalties, and even fraud allegations. For healthcare practices, understanding what upcoding is and how to prevent it is critical to maintaining compliance and financial stability. What Is Upcoding in Medical Billing? Upcoding occurs when a provider bills insurance for a service at a higher reimbursement rate than what was delivered. This usually happens by: • Assigning a more complex CPT code than the documentation supports • Submitting claims for services that were more intensive or time-consuming than actually provided • Using modifiers incorrectly to inflate reimbursement Example: A provider bills for a 60-minute patient evaluation (99215) when the visit lasted only 25 minutes (99213). Why Upcoding Is a Serious Compliance Risk Upcoding isn’t just a billing error—it can be viewed as fraud under federal law. The risks include: • Legal exposure: Practices may face lawsuits under the False Claims Act. • Financial penalties: Fines can reach up to three times the overbilled amount. • Loss of reputation: Investigations damage patient trust and payer relationships. • Audit risk: Payers and government agencies closely monitor coding patterns. Even if upcoding is unintentional, regulators may still treat it as fraudulent activity. Common Causes of Unintentional Upcoding Many practices don’t set out to commit fraud. Instead, errors usually happen due to: • Insufficient documentation – Notes don’t match the level of service billed. • Complex coding guidelines – Providers and staff may struggle with evolving CPT/ICD-10 rules. • Over-reliance on EHR templates – Automated code suggestions may default to higher levels of service. • Lack of training – Staff unaware of compliance standards can make mistakes. How to Prevent Upcoding in Your Practice To protect your practice from legal and financial consequences: • Ensure accurate documentation: Providers must record details that justify the billed service. • Invest in staff training: Ongoing coding and compliance education reduces errors. • Perform regular audits: Internal reviews catch mistakes before payers do. • Leverage credentialing support: Working with experts in Medical Credentialing California helps ensure providers are properly authorized and follow payer requirements. • Use compliance software: Tools with claim scrubbing and coding checks minimize risks. Legal Exposure Due to Unintentional Fraud The biggest fear for many practices is being accused of fraud when mistakes were simply unintentional. Upcoding—even when accidental—can trigger costly investigations. By taking proactive steps to ensure compliance, providers reduce their legal exposure while protecting revenue streams. FAQs About Upcoding in Medical Billing 1. What’s the difference between upcoding and unbundling? • Upcoding bills for a higher-level service than provided. • Unbundling splits services that should be billed together. Both are considered compliance risks. 2. Can upcoding happen accidentally? Yes. Many cases occur due to documentation gaps, coding complexity, or EHR errors rather than intentional fraud. 3. Who investigates upcoding cases? Medicare, Medicaid, private insurers, and the Office of Inspector General (OIG) may all audit claims for upcoding. 4. How can practices protect themselves from upcoding audits? Conduct regular internal audits, train staff on coding accuracy, and ensure documentation fully supports billed services. Final Thoughts Upcoding may seem like a small error, but its consequences are significant. Whether accidental or intentional, it exposes providers to legal, financial, and reputational risks. By prioritizing accurate documentation, regular compliance checks, and proper credentialing, practices can protect themselves and build long-term trust with payers and patients alike.
Introduction: Why EOBs Confuse So Many Patients If you’ve ever opened a letter from your insurance company after a doctor’s visit and thought, “Wait, I still have to pay this?”, you’re not alone. This document — called an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) — is one of the most misunderstood parts of the medical billing process. In this guide, we’ll break down what an EOB really means, why it matters, and how small practices can use this tool to improve transparency with patients. What Is an Explanation of Benefits (EOB)? An EOB is a statement sent by your health insurance provider after a healthcare service is processed. It is not a bill — it’s an informational summary showing: The services performed What your provider charged What your insurance covered Any amount you may owe to the provider Key Parts of an EOB While EOB layouts vary by insurance company, most include the following sections: Section What It Tells You Patient Information Name, date of service, and provider details Services Provided CPT or ICD-10 codes, procedure descriptions Amount Billed The provider’s original charge Allowed Amount The negotiated rate insurance will pay Insurance Payment How much your plan covered Patient Responsibility Your copay, coinsurance, or deductible Remarks/Notes Additional clarifications or denial reasons Common Reasons Patients Misunderstand EOBs Patients often confuse an EOB with a bill because: The layout looks like an invoice — with numbers in bold. Insurance language can be full of abbreviations and codes . It lists an “Amount You Owe” without explaining payment instructions. For small practices, unclear EOB explanations can lead to: More billing-related phone calls Delayed payments from patients Frustration that affects patient satisfaction How Small Practices Can Help Patients Read EOBs Clear communication about EOBs can improve collections and trust. Best practices include: Providing a quick reference guide for reading EOBs Highlighting “This is not a bill” in patient communications Offering billing consultations for high-cost services Using patient portals to link EOBs with billing records (Related: Medical Billing for Small Practices) EOB vs. Medical Bill — The Key Difference EOB Medical Bill Sent by insurance company Sent by provider or billing company Explains what insurance covered Requests payment from the patient Includes codes & claim details Lists actual amount due No payment action required Payment action required Why EOB Accuracy Matters A mistake on an EOB can lead to incorrect patient balances or claim denials. Practices should: Verify CPT & ICD-10 codes before claims submission Follow up on discrepancies immediately with insurers Keep documentation of all communications for appeals Final Takeaway An Explanation of Benefits is a valuable tool for both patients and providers — if it’s understood correctly. By helping patients interpret their EOBs, small practices can reduce confusion, speed up payments, and improve overall satisfaction. If your practice struggles with billing transparency or wants to improve patient payment timelines, outsourcing medical billing can streamline the process and ensure EOB accuracy from the start.
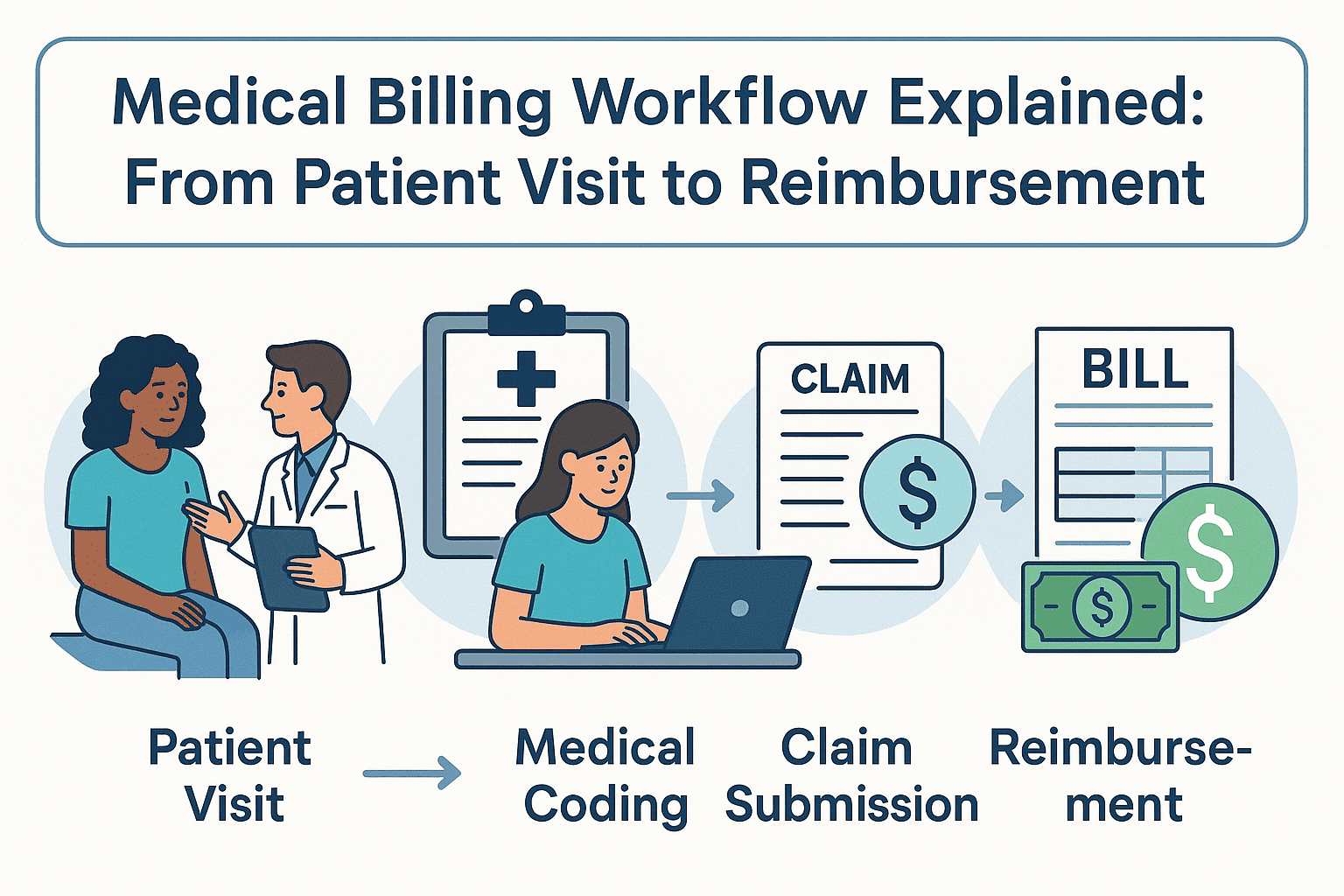
Efficient medical billing isn’t just about submitting claims — it’s about managing the entire revenue cycle from the moment a patient checks in to the day the reimbursement lands in your account. Whether you're a provider or practice manager, understanding this end-to-end medical billing workflow can help you reduce denials, get paid faster, and improve patient satisfaction. This step-by-step guide breaks down the entire workflow, using plain language and real pain points — from registration to reimbursement. Step 1: Patient Registration and Insurance Eligibility Verification The workflow starts before the patient even meets the provider. Front-desk staff collect: • Full name, date of birth, contact details • Insurance provider, plan ID, and group number • Referral or authorization (if needed) • Copay and deductible details Insurance eligibility verification is critical. If a patient’s coverage isn’t active or doesn’t match the services rendered, the claim will likely be denied — leading to revenue loss and patient frustration. Step 2: Accurate Medical Coding with ICD-10 and CPT Codes Once the visit is complete, the provider’s notes are translated into standardized codes: • ICD-10 codes represent diagnoses • CPT codes represent procedures or services • HCPCS codes may be used for medical supplies or drugs These codes must be assigned accurately based on documentation. Errors at this stage result in denied or underpaid claims. Want to understand how California regulations impact your coding strategy? Explore Medical Billing and Coding California for regional best practices. Step 3: Charge Entry and Clean Claim Generation The next step is charge entry — inputting all relevant billing details into the practice management system: • Patient demographics • Provider details • Diagnosis and procedure codes • Date of service and billed charges Once completed, a clean claim is generated. Clean claims are error-free and ready for submission, which helps reduce rework and accelerates reimbursement. Step 4: Electronic Claim Submission to Insurance Payers Claims are transmitted to payers — usually via clearinghouses — using electronic data interchange (EDI). This step includes: • Validating claim format • Scrubbing for missing or mismatched information • Submitting to government (e.g., Medicare/Medicaid) or private payers Common issues that delay submission: • Invalid patient ID numbers • Missing modifiers • Service date mismatches Step 5: ERA Posting and Explanation of Benefits (EOB) Processing Once payers process the claim, they issue: • Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA) — a digital explanation of payment • Explanation of Benefits (EOB) — a patient-facing summary of what’s covered The medical billing team posts payments into the system, reconciles amounts, and flags any shortfalls or denials for follow-up. Step 6: Denied Claims and Appeals Workflow Not every claim is approved the first time. Common denial reasons include: • Coding errors or mismatches • Lack of medical necessity • Missing clinical documentation • Services not covered under the plan Denied claims must be corrected, appealed, and resubmitted — often within strict payer deadlines. A well-trained billing team ensures your practice doesn’t lose money on technicalities. Step 7: Final Patient Billing, Collections, and Balance Follow-Up After the insurer has paid its share, patient responsibility comes into play: • Statements are sent with clear breakdowns • Payment options and portals are provided • Reminder systems follow up on unpaid balances Offering flexible payment plans or financial counseling can improve collection rates and patient satisfaction. Why Following a Medical Billing Workflow Improves Reimbursement Every step in this workflow exists for a reason. Skipping or rushing through even one can cause delays, denials, or compliance issues. A structured process helps your practice: • Reduce claim rejections and denials • Speed up cash flow and A/R cycles • Ensure payer compliance and audit readiness • Enhance the patient experience For practices in states like California, where compliance is strict and payer networks are diverse, a streamlined workflow is essential. Learn more at Medical Billing and Coding California . FAQs About Medical Billing Workflows What is the full medical billing process? It’s a seven-step process that includes registration, coding, charge entry, claim submission, payment posting, denial management, and patient billing. What are the 7 steps in medical billing workflow? 1. Patient registration and eligibility verification 2. Medical coding (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS) 3. Charge entry and claim creation 4. Electronic claim submission 5. Payment posting with ERA and EOB 6. Denial management and appeals 7. Patient billing and collections Why do insurance claims get denied? Claims are denied due to coding errors, missing information, expired coverage, or failure to meet medical necessity guidelines. What’s the difference between medical coding and billing? Coding converts clinical notes into standardized codes. Billing uses those codes to submit claims and collect payments. How do you improve your billing cycle efficiency? Use trained coders, verify insurance early, automate reminders, and conduct regular audits. Consider outsourcing to experts for better cash flow. Conclusion: Streamlining Your Medical Billing Process for Financial Success Understanding and refining your medical billing workflow is more than a backend function — it’s a strategic necessity. By training your team, using accurate codes, and following a defined process, your practice can maximize reimbursements, stay compliant, and deliver a better experience for both staff and patients.

In medical offices across the U.S., one of the most common sources of confusion among staff—especially new admin and billing coordinators—is the difference between CPT codes and ICD-10 codes . These two types of medical codes serve entirely different purposes, and mixing them up can lead to claim denials , billing errors , and compliance risks . Whether you're a healthcare provider, front office staff, or billing team member, this guide explains what each code type means, how they work together, and why getting them right is essential—especially if you're billing in states like California, where payer rules can be even more specific. Why Staff Often Confuse CPT and ICD-10 Codes Here’s a typical situation in a clinic: A provider documents a diagnosis and a procedure, and the billing staff must translate that into the right code combination. But: A new staff member might use a diagnosis code (ICD-10) where a procedure code (CPT) is required. Some claim rejections don’t clearly say what was wrong—just “coding mismatch.” Training materials often lump all “codes” together without breaking down use cases. This coding confusion delays reimbursement, increases workload, and may even flag audits. CPT Codes vs ICD-10 Codes: Key Differences You Need to Know Let’s break it down clearly: 1. What Are CPT Codes? Stands for : Current Procedural Terminology Used for : Procedures and services performed (e.g., office visits, surgeries, tests) Maintained by : American Medical Association (AMA) Examples : 99213 – Office/outpatient visit, established patient 71045 – Chest X-ray 93000 – EKG 2. What Are ICD-10 Codes? Stands for : International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision Used for : Diagnoses (the reason a service was provided) Maintained by : World Health Organization (WHO) Examples : E11.9 – Type 2 diabetes without complications J01.90 – Acute sinusitis M54.5 – Low back pain 3. CPT Codes = What Was Done | ICD-10 Codes = Why It Was Done You need both for a clean claim: ICD-10 tells the payer why the patient needed care. CPT tells them what care was provided. If you only include one or mismatch them, the claim may be denied or delayed. Why This Coding Distinction Matters in California Billing In states like California, where payer policies vary widely across private insurers, HMOs, and Medi-Cal, accurate coding is even more critical. Errors in CPT/ICD-10 combinations can result in: Rejected claims from Anthem, Blue Shield, or Kaiser Denied Medi-Cal encounters due to invalid code pairings Payment delays due to "unspecified" diagnosis codes Staff training in medical billing and coding California guidelines often highlights how stricter regional payer edits increase the need for coding accuracy. How to Prevent Coding Errors in Your Practice If your front desk or billing staff struggle to match CPT and ICD-10 codes correctly, here’s how to reduce errors: Use coding crosswalk tools that link common ICD-10 codes with typical CPT services. Review denied claims monthly to identify recurring coding mismatches. Train new staff using real-life claim examples, not just theoretical scenarios. Use certified billing partners who stay updated on California-specific coding changes. FAQs: CPT vs ICD-10 Coding Questions Can I submit a claim with just an ICD-10 code? No. A claim must include at least one CPT code to show the service rendered. ICD-10 codes alone explain the diagnosis, not the work done. What happens if the CPT and ICD-10 codes don’t align? Misalignment often results in a claim denial with a vague remark code. This means manual rework, delayed payments, and often, patient confusion. Are CPT and ICD-10 codes updated yearly? Yes. Both sets are updated annually. CPT codes usually update in January, while ICD-10 codes update in October. Always use the most current versions to avoid denials. Where can staff learn proper medical coding? In-house training, AAPC-certified courses, or working with a professional medical billing and coding California team can provide accurate, ongoing education. Final Thought The difference between CPT codes and ICD-10 codes isn’t just technical—it directly impacts how quickly your clinic gets paid and how smoothly your operations run. Accurate coding reduces denials, protects against audits, and ensures staff confidence when handling claims. If your clinic is located in a complex payer landscape like California and struggling with staff coding accuracy, it may be time to consult a trusted medical billing and coding California service. The right support team will help you eliminate guesswork and secure faster reimbursements.
Reading a medical bill shouldn't require a medical degree, yet many patients and even admin staff find them hard to understand. This guide explains how to read a medical bill clearly, so you know what you’re being charged for and why—and how to avoid overpaying or getting lost in billing errors. Why Medical Bills Are So Confusing for Patients and Staff A common frustration patients express is: “Why am I getting billed after already paying at the clinic?” “What does this CPT code even mean?” For admin staff, explaining vague charges or denied claims without full context leads to tension, especially during high call volumes. Miscommunication slows down payment collections and lowers patient satisfaction. Understanding medical bill terminology helps solve both patient confusion and front-office stress. How to Read a Medical Bill: Line-by-Line Breakdown Let’s walk through how to read each part of a standard medical bill, so both patients and staff can confidently understand the charges. 1. Patient Information and Service Dates Start by confirming the basics: patient name, provider, and date of service. Errors here could mean you're reviewing the wrong bill entirely. 2. Understanding CPT Codes on Medical Bills Every medical bill includes CPT codes —Current Procedural Terminology. These are standard codes that describe services like office visits, lab tests, or procedures. Patients may not recognize them, but they’re essential for decoding services and insurance claims. Tip for admin staff : Use your billing software to explain CPT codes in plain English, especially for frequently asked codes like 99213 (office visit) or J1885 (injection). 3. Billed Amount vs. Allowed Amount: What's the Difference? Billed Amount : What the provider charges. Allowed Amount : What your insurance agrees to pay. The gap between these amounts is often adjusted, denied, or passed to the patient based on coverage and deductibles. This is where most confusion begins. 4. How Insurance Payments and Adjustments Work This section shows what your insurance provider paid , what they adjusted (or wrote off), and what’s left for you. Compare this to your Explanation of Benefits (EOB) for accuracy. Discrepancies here are often due to authorization issues or out-of-network care. 5. Understanding Patient Responsibility in Medical Billing This final section shows what the patient owes. If something seems off—a denial, duplicate, or unusual charge—it’s worth digging into. What to Do When a Medical Bill Looks Wrong It’s estimated that over 80% of medical bills contain at least one error. Whether you're a patient or a clinic manager, here’s what you should do: Request an itemized bill. This shows each service and corresponding charge, not just totals. Compare with your EOB. Ensure services and amounts match what your insurer reported. Contact the billing department directly. Don’t rely solely on front desk or reception—ask to speak with someone from billing or collections. Common CPT Billing Codes Patients Ask About Understanding a few common codes can help you identify unnecessary or duplicate charges: CPT Code | Description -----------|-------------------------------------------- 99213 | Established patient office visit 80050 | General health panel (lab work) J1885 | Ketorolac injection (non-opioid pain) These codes are often misunderstood and lead to billing disputes if not explained clearly. When to Consider Help with Medical Billing If billing is a constant challenge in your clinic—or you’re a patient dealing with multiple unclear bills—it's worth exploring professional help. Many providers use Medical Billing Services Near Me to manage claim denials, clarify patient balances, and improve collection rates. FAQs: What People Also Ask About Medical Bills How do I read a medical bill from my provider? Start by checking patient information, CPT codes, billed vs. allowed amounts, and compare it to your Explanation of Benefits (EOB). If something looks off, request an itemized bill. Why did my insurance not cover a medical bill? Possible reasons include using an out-of-network provider, not meeting your deductible, or lack of prior authorization. Contact your insurer for detailed reasons. Can patients dispute medical charges? Yes. You can appeal insurance denials, request billing reviews, and even negotiate payment amounts—especially if you're uninsured. What's the difference between an EOB and a medical bill? An EOB is a statement from your insurer explaining what was covered. A medical bill is from your provider, showing what you owe after insurance adjustments. Final Thoughts Learning how to read a medical bill gives patients more control and helps admin staff provide better service. By breaking down codes, charges, and responsibilities, you can reduce billing stress—and avoid paying more than you should. And if your clinic’s billing process still causes confusion, it might be time to work with experienced medical billing services to simplify patient communication and speed up collections.